The successful deployment of the solar sail is seen as a critical step forward in space exploration technology, with potential applications for future deep-space missions and scientific explorations. For more details, you can read the full articles on NASA’s official website and Phys.org.
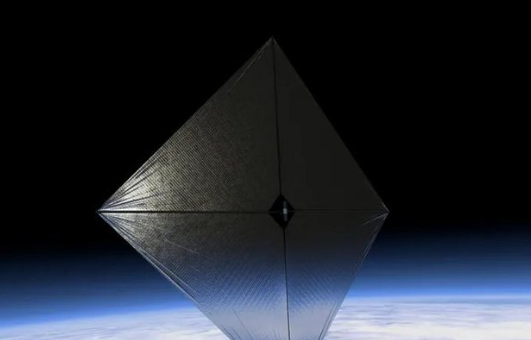
More than four months after its launch, NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System (ACS3) has successfully deployed its solar sail in space. The ACS3 hitched a ride to space on Rocket Lab’s Electron vehicle on April 24, and NASA confirmed at the end of August that the spacecraft had fully deployed its sail. On August 29, at 1:33 p.m. EDT, mission operators received data confirming the success of the sail’s deployment and boom system.
NASA’s solar sail successfully spreads its wings in space.
More than four months after launching to space, a solar-sailing spacecraft has successfully spread its wings above our planet.#NASA #Starlink #ElonMusk #Crypto #IndependenceDay2024 #TheGOAT #Venezuela #Bitcoin2024 pic.twitter.com/KZ0fRRW7aO
— TRADER Lover 77 (@Iamtrader77) August 31, 2024
Solar sails operate much like traditional sails on a sailboat, but instead of harnessing wind, they use sunlight to propel through space. Although photons from the sun lack mass, they carry momentum, which, upon striking the sail, generates a small but continuous force that propels the spacecraft forward. The ACS3 is equipped with four cameras capable of capturing panoramic views of the reflective sail and its composite booms. High-resolution images from these cameras are expected to be available on September 4.
In the coming weeks, the solar sail will undergo a series of tests to evaluate its maneuverability in space. By adjusting its orbit, researchers aim to gather valuable data that could help design and operate future solar-sail-equipped missions. These findings could have significant implications for space weather early-warning systems, asteroid reconnaissance, and missions to observe the sun’s polar regions.
NASA is optimistic that the data gathered from the ACS3 mission will pave the way for larger-scale solar sail systems in the future. The potential applications for this technology are vast, ranging from providing early warnings about space weather to exploring small celestial bodies and even monitoring the sun’s polar regions.
Sail deployment in space achieved! 🛰️☀️⛵@NASA is sailing on sunshine, and so are we after seeing the ACS3 satellite successfully unfurl its 80m2 (860sqft) solar sail in orbit yesterday, completing its primary mission objective!
Pics from the satellite will come Sep. 4th. 😉 pic.twitter.com/Qh3CHLnU9A
— Kongsberg NanoAvionics (@NanoAvionics) August 30, 2024
The ACS3 is currently orbiting the Earth at an altitude roughly twice that of the International Space Station. From above, the sail resembles a square about half the size of a tennis court, covering approximately 860 square feet (80 square meters). This deployment marks a significant milestone for solar sail technology, which could revolutionize the way we explore and utilize space.
Key Points:
i. NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System (ACS3) has successfully deployed its solar sail in space.
ii. The solar sail harnesses the momentum of sunlight to propel the spacecraft through space.
iii. The mission aims to test the maneuverability of solar sails and gather data for future missions.
iv. Potential applications include space weather monitoring, asteroid reconnaissance, and solar observation.
v. The ACS3’s successful deployment marks a significant step forward in the development of solar sail technology.
James Kravitz – Reprinted with permission of Whatfinger News